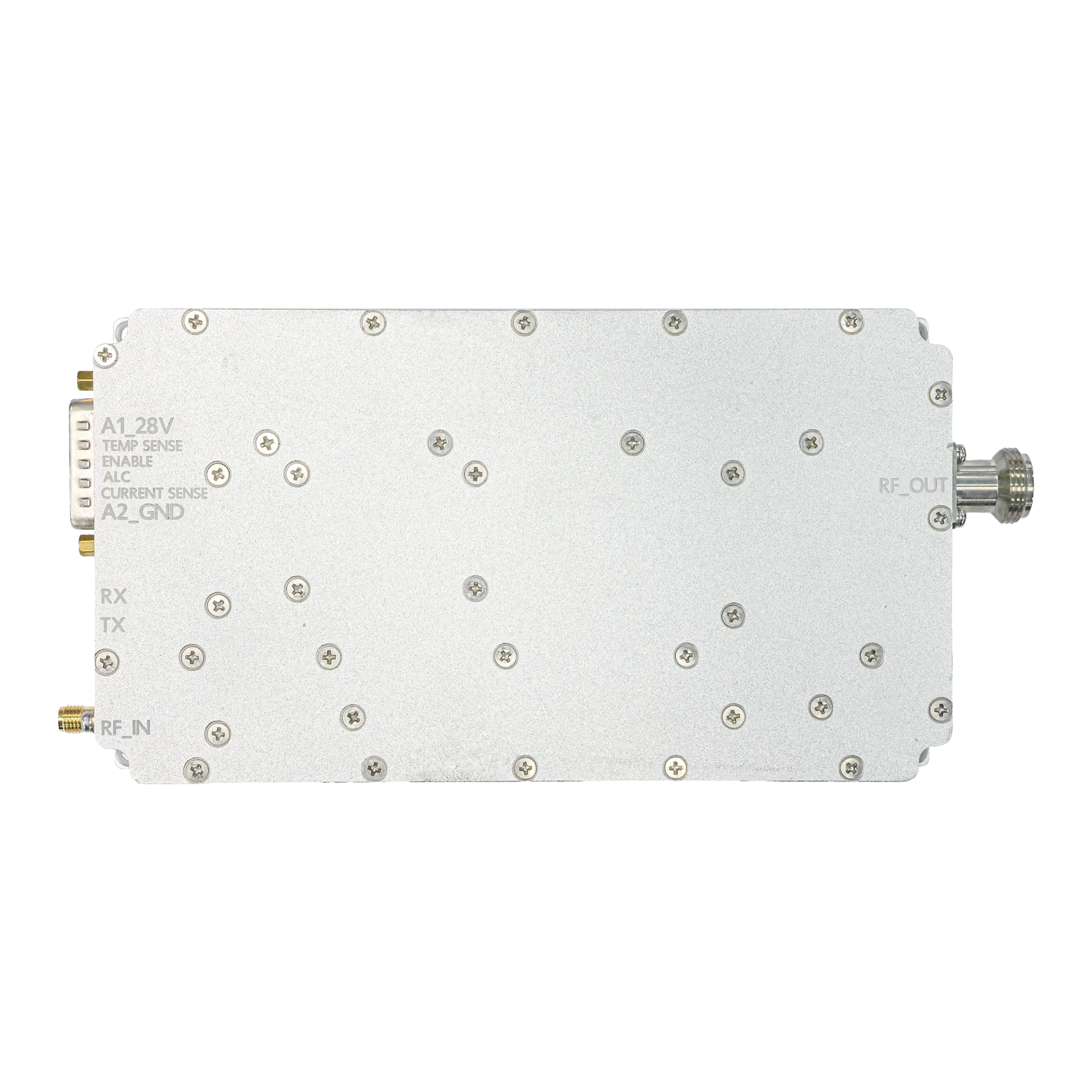
RF Transmitter & Receiver Modules High-Range 2.4GHz Wireless Kits
- Understanding the Fundamentals of RF Communication Systems
- Technical Advantages in Modern Transceiver Modules
- Performance Benchmarking: Leading Manufacturers Compared
- Customization Strategies for Specific Use Cases
- Real-World Applications Across Industries
- Optimizing Signal Integrity in Noisy Environments
- Future Trends in 2.4 GHz RF Transmitter and Receiver Technology
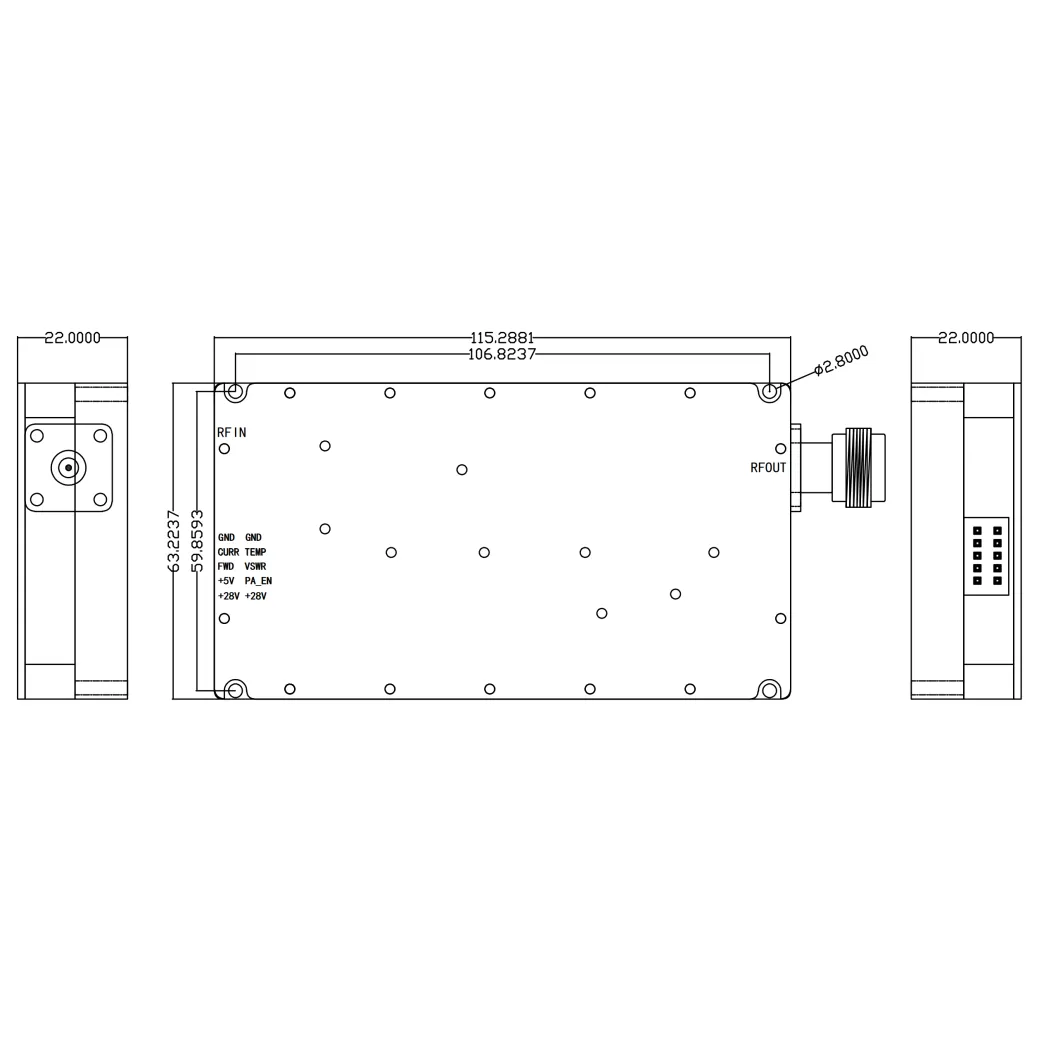
(about rf transmitter and receiver)
Understanding the Fundamentals of RF Communication Systems
Radio Frequency (RF) transmitter and receiver modules form the backbone of wireless communication, converting electrical signals into electromagnetic waves for data transmission. These systems operate across frequencies from 315 MHz to 2.4 GHz, with 2.4 GHz modules dominating modern applications due to their balance between range (typically 100-500 meters) and obstacle penetration capabilities.
Technical Advantages in Modern Transceiver Modules
Contemporary RF modules integrate three critical innovations:
- Adaptive Frequency Hopping: Automatically switches between 80 channels to avoid interference
- Low-Energy Protocols: Consumes 12-18 mA during transmission vs. 30 mA in legacy systems
- Enhanced Modulation: Achieves 2 Mbps data rates through GFSK encoding
Performance Benchmarking: Leading Manufacturers Compared
| Model | Frequency | Range | Power Consumption | Price (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RFM69HW | 433/915 MHz | 1,200 m | 130 mA | $8.50 |
| NRF24L01+ | 2.4 GHz | 800 m | 12.3 mA | $3.20 |
| CC1101 | 315-915 MHz | 300 m | 30 mA | $6.80 |
Customization Strategies for Specific Use Cases
Industrial applications demand ruggedized modules with -40°C to +85°C operational ranges, while consumer electronics prioritize compact designs under 15mm². Automotive-grade solutions require compliance with AEC-Q100 standards and 5kV ESD protection.
Real-World Applications Across Industries
- Smart Home Systems: 92% of Z-Wave hubs utilize 908.42 MHz receivers
- Drone Telemetry: 2.4 GHz modules enable 7ms latency for FPV racing
- Industrial IoT: 868 MHz transmitters achieve 98.7% packet success in metal-rich environments
Optimizing Signal Integrity in Noisy Environments
Advanced modules implement dual-stage filtering (30 dB suppression at 10 MHz offset) and automatic gain control (AGC) with 64 dB dynamic range. Directional antennas improve SNR by 18 dB in urban deployments.
Future Trends in 2.4 GHz RF Transmitter and Receiver Technology
The next generation of RF modules will integrate AI-driven spectrum allocation, reducing collision probability by 73% in dense networks. Emerging Wi-Fi 6E compatibility enables seamless handoff between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands, while gallium nitride (GaN) amplifiers promise 55% efficiency gains over silicon-based designs.

(about rf transmitter and receiver)
FAQS on about rf transmitter and receiver
Q: What is the basic function of an RF transmitter and receiver module?
A: RF transmitter and receiver modules wirelessly transmit and receive data signals. The transmitter encodes data into radio waves, while the receiver decodes them to recreate the original information.
Q: What are common applications of 2.4 GHz RF transmitter and receiver modules?
A: These modules are widely used in remote-controlled devices like drones, garage openers, and IoT systems. The 2.4 GHz frequency offers better range and reduced interference compared to lower frequencies.
Q: How does an RC transmitter differ from standard RF modules?
A: RC transmitters are optimized for real-time control applications with low latency. They often include features like multiple channels and failsafe mechanisms for reliable operation in robotics or hobby projects.
Q: Can 2.4 GHz RF modules interfere with Wi-Fi signals?
A: Yes, since both operate on the 2.4 GHz ISM band. However, modern modules use frequency-hopping spread spectrum (FHSS) technology to minimize interference and maintain stable communication.
Q: What factors affect the range of RF transmitter and receiver systems?
A: Range depends on transmission power, antenna design, and environmental obstacles. Most consumer-grade 2.4 GHz modules achieve 100-500 meters in open spaces, reduced by walls or electromagnetic interference.
-
09 March 2021 21 May 2025
-
09 March 2021 16 May 2025
-
09 March 2021 16 May 2025
-
09 March 2021 16 May 2025
-
09 March 2021 16 May 2025
-
09 March 2021 21 May 2025
-
09 March 2021 25 Dec 2024
-
09 March 2021 14 Oct 2022
-
09 March 2021 25 Dec 2024